The Metacarpophalangeal Joints at the Base of the Fingers Are
Extensive musculature stabilizes these joints. The humeroulnar joint c.
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_sm.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/metacarpophalangeal-joints-3/R6Q09HKClnxIkdN9k5mT5g_metacarpophalangeal_joint.png)
Metacarpophalangeal Mcp Joints Bones And Ligaments Kenhub
Silicone arthroplasty is indicated in.
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_sm.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/metacarpophalangeal-joints-3/R6Q09HKClnxIkdN9k5mT5g_metacarpophalangeal_joint.png)
. Metacarpophalangeal Joint MCP Joint The MP joint is where the hand bone called the metacarpal meets the finger bones called the phalanges. Proximal interphalangeal joint PIP the joint in the middle of the finger. These complex hinge joints are important for both power grip and pinch activities.
Also called the knuckle this is where the finger bones meet the hand bones. They are responsible for a wide range of movements including flexion extension abduction adduction and circumduction. The basic structure of the MCP joint of the thumb is similar to that of the fingers.
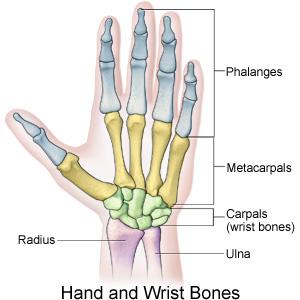
The metacarpophalangeal joints connect the metacarpal bones to the proximal phalanges of the digits. The collateral ligaments are loose when the joint is. The joint at which the finger becomes separate from the hand.
Distal interphalangeal joint DIP the joint closest to the fingertip. MCP joint arthritis is most common in the thumb and index fingers due to the stress of pinching. Each metacarpal bone connects to one finger or a thumb at a joint called the metacarpophalangeal joint or MCP joint.
Active and passive motions at the MCP joint of the thumb are significantly less than those at the MCP joints of the fingers. They act as complex hinge joints and are important for both power grip and pinch activities. The three joints of your fingers are.
MCP joints are important for both pinching and gripping. Chung Abstract The metacarpophalangeal MCP and proximal interphalangeal PIP joints can be deformed and disabled by arthritis. The metacarpophalangeal joint MCP joint or knuckle is where the finger bones meet the hand bones.
Causes of Metacarpophalangeal Joint Arthritis. The metacarpophalangeal joint of the index finger of the right hand is placed against the transverse process of the sixth cervical vertebra and the thumb is kept extended to avoid the patients trachea. Compare the joint structure of the metacarpophalangeal MCP joints with that of the interphalangeal IP joints of the fingers.
On each finger and the thumb a metacarpal bone connects to the proximal phalanx. The finger MP joints have an oval convex metacarpal surface that articulates with a concave shallow proximal phalangeal surface. For all practical purposes the MCP joint of the thumb allows only 1 degree of freedom.
The surfaces of the bones where they meet to form joints are covered with a layer of cartilage which allows them to glide smoothly against one another as they move. The MP joints are less often affected by arthritis than the smaller joints in the hand or the joints where the thumb joints the wrist CMC. Proximal interphalangeal joint PIP.
Being condyloid they allow the movements of flexion extension. The articulating surface of each metacarpal head and proximal phalange is composed of hyaline cartilage. At the base of each finger there are large joints in the hand known as the matacarpophalangeal MP or MCP joints.
The MP joints are less often affected by arthritic conditions than the smaller joints in the hand or the joint where the thumb joins the wrist CMC. They are deliberately engineered to crowd each other when flexed simultaneously and friction between the sides of fingers is essential to. Treatment is challenging owing to bony destruction and tendon imbalances.
One example of a multiaxial joint. The metacarpophalangeal joints MCP are situated between the metacarpal bones and the proximal phalanges of the fingers. Despite their structural similarities these joints are much less restricted in motion compared to the first MP joint of the thumb.
Identify both similarities and differences. At the MCP joint the fingers can move in multiple directions. Each metacarpophalangeal joint is formed by the convex heads of the.
The fingers can only flex and extend except at the metacarpophalangeal joints where abduction and adduction are controlled by the intrinsic hand muscles. They act as complex hinge joints and are important for both power grip and pinch activities. The metacarpophalangeal joints at the base of the fingers are _____ joints.
The base of the proximal phalanx is displaced over the dorsum of the metacarpal head. The large joints in the hand at the base of each finger are known as the metacarpophalangeal MP or MCP joints see Figure 1. The condyles of each phalangeal head are shaped in such a way that when each finger is flexed at the MCP and interphalangeal joints the fingertips point toward a common point near the base of the thumb.
The metacarpophalangeal joints MCP are a collection of condyloid joints that connect the metacarpus or palm of the hand to the fingers. Back of the metacarpal head to the front of the base of the proximal phalanx. These joints are of the condyloid kind formed by the reception of the rounded heads of the metacarpal bones into shallow cavities on the proximal ends of the proximal phalanges.
The large joints in the hand at the base of each finger are known as the metacarpophalangeal MP or MCP joints see Figure 1. Complete dorsal dislocation of the metacarpophalangeal joint of the index finger is rare and closed reduction of this peculiar dislocation is usually impossible. Reconstruction of a stable mobile pain-free joint is crucial to restore hand function.
The talocrural joint d. The metacarpophalangeal MP or MCP joints are large joints at the base of each finger. They can bend straighten spread apart and move together.
The carpal bone that connects to the thumbs MCP joint is the trapezium. A System of Orthopaedic Medicine Third Edition 2013. Any metacarpophalangeal joint b.
All individuals are unique. Sasor and Kevin C. The metacarpophalangeal MCP joints are diarthrodial joints where the large convex heads of the distal aspect of the metacarpals articulate with the concave-shaped proximal aspect of each phalange.
They act as complex hinge joints and are important for both pinch and power grip activities. Finger MP joints. This joint is commonly referred to as the knuckle joint.
The bones in our fingers and thumb are called phalanges. The injury is produced by striking of the outstretched index against a resistant object usually in a fall on the hand. MP joints are important for both power grip and pinch activities and are where the fingers move with respect to the hand.
A single hand bone is called a phalanx. The MP joints are less often affected by arthritic conditions than the smaller joints in the hand or the joint where the thumb joins the wrist CMC. The atlanto-occipital joint e.
Metacarpophalangeal joint MCP the joint at the base of the finger. The MP joints are not affected as much by arthritic conditions as the smaller joints in the hand or the joint where the thumb joins the wrist. There are five separate metacarpophalangeal joints that connect each metacarpal bone to the corresponding proximal phalanx of each finger.
This is the joint in the middle. What is the metacarpophalangeal MP joint. Flexion and extension within the frontal plane.
Goniometry Thumb Metacarpophalangeal Joint Flexion And Extension Physiopedia
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13243/aaa_copy.png)
Metacarpophalangeal Mcp Joints Bones And Ligaments Kenhub

Comments
Post a Comment